FluentD vs FluentBit - Which log collector to choose?
Tools like Fluentbit and Fluentd make log management more efficient by centralizing log data from multiple sources and providing the ability to monitor and analyze it all in one place.

Log management is the practice of collecting, storing, analyzing, and monitoring log data from various systems and applications. This log data can provide valuable insights for organizations such as identifying system issues, troubleshooting problems, detecting security threats, and meeting compliance requirements.
In this article, we will be talking about the two very famous log aggregators - Fluentd and Fluent Bit. Fluentd and Fluent Bit are open-source log management tools that are designed to collect, store, and analyze log data.
Fluentd is a more feature-rich tool with a robust plugin system, written in Ruby, and can process, transform, and forward log data to various systems. Fluent Bit is a lightweight, performant tool written in C and focuses on low resource usage, serving highly distributed environments where limited capacity and reduced overhead (memory and CPU) are a huge consideration, making it suitable for edge computing and IoT use cases.
Both tools have active communities and support a variety of integrations, organizations can choose the one that fits their specific requirements. Let’s compare the two in depth.
Key Differences between Fluentd and Fluent Bit
Performance
Performance is one of the key factors that organizations consider when choosing between Fluentd and Fluentbit. Both tools have different performance characteristics when it comes to latency and throughput.
1. Throughput
- Fluentd: Fluentd can handle a high throughput of data, as it can be scaled horizontally and vertically to handle large amounts of data. Its plugin system allows for handling large amounts of data.
- Fluent Bit: Fluent Bit also can handle a high throughput of data. It's designed to be lightweight and with low resource usage, which means it can be deployed in large numbers of small instances, which can help to handle a high throughput of data.
2. Latency
- Fluentd: Latency in Fluentd is generally higher compared to Fluentbit. This is due to the fact that Fluentd processes and transforms log data before forwarding it, which can add to the latency.
- Fluent Bit: Fluent Bit is designed to be highly performant, with low latency. It is lightweight and has minimal overhead, which makes it well-suited for edge computing and IoT use cases where low latency is important.
Resources such as memory and CPU usage
Fluentd and Fluentbit have different resource usage characteristics when it comes to memory and CPU. Fluentd uses more memory and CPU resources than Fluentbit. Fluentd has a larger codebase and additional features, which can increase its memory and CPU usage. Fluentbit, on the other hand, is designed to be lightweight and with low resource usage, which helps keep its memory and CPU usage low. This makes Fluentbit a more suitable option for use cases where resource usage is a concern, such as edge computing and IoT.
Scalability
Scalability is another important factor to consider when comparing Fluentd and Fluent Bit. Both tools can be scaled horizontally and vertically to handle large amounts of data, but they have different scalability characteristics.
1. Horizontal Scaling
- Fluentd: Fluentd can be horizontally scaled by adding more instances of Fluentd running on different machines. This can be done by using a load balancer to distribute incoming data to multiple Fluentd instances.
- Fluent Bit: Fluent Bit can also be horizontally scaled by adding more instances running on different machines. Fluent Bit uses a smaller footprint, which means that it can be deployed in a large number of small instances which can handle a high throughput of data.
2. Vertical Scaling
- Fluentd: Fluentd can be vertically scaled by increasing the resources of a single instance, such as adding more CPU and memory.
- Fluent Bit: Fluent Bit can also be vertically scaled by increasing the resources of a single instance, such as adding more CPU and memory, but due to its minimal overhead, it might require fewer resources to handle the same amount of data compared to Fluentd.
Features
1. Input and output plugins
Both Fluentd and Fluent Bit provide a wide range of input and output plugins that allow you to collect data from various sources, such as log files, databases, message queues, and cloud services, and forward them to different destinations, such as files, databases, message queues, and cloud services. This allows you to collect and process data from different sources and forward it to the desired location for further analysis and storage. Fluentd has around 650 plugins, and Fluent Bit has only 35 plugins available.
2. Filter and transformation capabilities
Both Fluentd and Fluent Bit have filter and transformation capabilities, which allow you to process and modify data before it is forwarded to its final destination. This can include things like filtering out specific log levels, renaming fields, adding new fields, and more. This allows you to pre-process data to make it more useful for your specific use case.
3. Extensibility
In terms of extensibility, Fluentd has a larger community and ecosystem of plugins compared to Fluent Bit. This means that there are more plugins available for Fluentd, which can make it easier to add new functionality to your data collection and logging pipeline. Additionally, Fluentd has more advanced routing and buffering capabilities, which can be useful for managing and processing large amounts of data.
Fluent Bit, on the other hand, is written in C and is more lightweight and less resource-intensive compared to Fluentd. This makes Fluent Bit well-suited for use cases where low resource usage and high performance is needed, such as in embedded systems, edge computing, and IoT applications. Fluent Bit also has a smaller footprint and can be easily integrated into existing systems.
Community and support system
Both Fluentd and Fluent Bit have strong community support and a wide range of resources available for users. Fluentd has a larger and more established community with a more extensive ecosystem of plugins and integrations, while Fluent Bit has a smaller but growing and focused user base with strong support systems from the company.
Use cases of FluentD and FluentBit
- Logging and monitoring: Fluentd and Fluent Bit can be used to collect, process, and forward log data from various sources to a centralized location for analysis and storage. This can be used for monitoring the performance and stability of systems, as well as troubleshooting and debugging issues.
- Data integration: Fluentd and Fluent Bit can be used to collect and process data from different sources and forward it to different destinations. This can be used for integrating data from different systems and applications, such as databases, message queues, and cloud services.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Fluentd and Fluent Bit can be used to collect and process data from IoT devices and forward it to a centralized location for analysis and storage. Fluent Bit is particularly well suited for this use case due to its lightweight and low resource usage.
- Cloud-native: Fluentd and Fluent Bit can be used to collect, process, and forward data in cloud environments. Fluent Bit has been designed to work well in cloud-native environments and can be used in the Kubernetes cluster to collect and forward logs and metrics from the containers.
Fluentd and Fluent Bit are versatile data collection and logging tools that can be used in a wide range of use cases, such as logging and monitoring, data integration, stream processing, IoT, and cloud-native environments. Fluentd is more versatile and can handle more complex use cases, while Fluent Bit is more suitable for resource-constrained environments and cloud-native use cases.
Choosing between FluentD and FluentBit
In conclusion, Fluentd and Fluent Bit are both open-source data collection and logging tools that provide powerful and flexible ways to collect, process, and forward data from various sources to different destinations. They have similar features, such as input/output plugins, extensibility, and filter and transformation capabilities. However, Fluentd is more advanced in terms of routing and buffering capabilities and has a larger community and ecosystem of plugins, while Fluent Bit is more lightweight and well suited for resource-constrained environments, such as embedded systems, edge computing and IoT applications, and has a smaller but growing and focused user base.
All in all, Fluent Bit to Fluentd is more like beats to logstash - a lightweight shipper that can be installed as agents on edge hosts or devices in a distributed architecture. For e.g. in a Kubernetes environment, Fluent Bit can be deployed as a DaemonSet on each node to collect and forward data to a centralized Fluentd instance, acting as an aggregator, processing the data, and routing it to different sources based on tags, providing efficient and centralized management of the data collected from all nodes in the cluster. This setup allows for efficient resource utilization and flexibility in routing and processing data. Fluent Bit can be used on its own, of course but has far less to offer in terms of aggregation capabilities and a much smaller amount of plugins for integrating with other solutions.
Once the log data is collected and aggregated, you will need a centralized log management tool to store and analyze the logs. That’s where SigNoz comes in.
Log Analytics with SigNoz
SigNoz is a full-stack open-source APM that can be used as a log management tool. SigNoz uses a columnar database ClickHouse to store logs, which is very efficient at ingesting and storing logs data. Columnar databases like ClickHouse are very effective in storing log data and making it available for analysis.
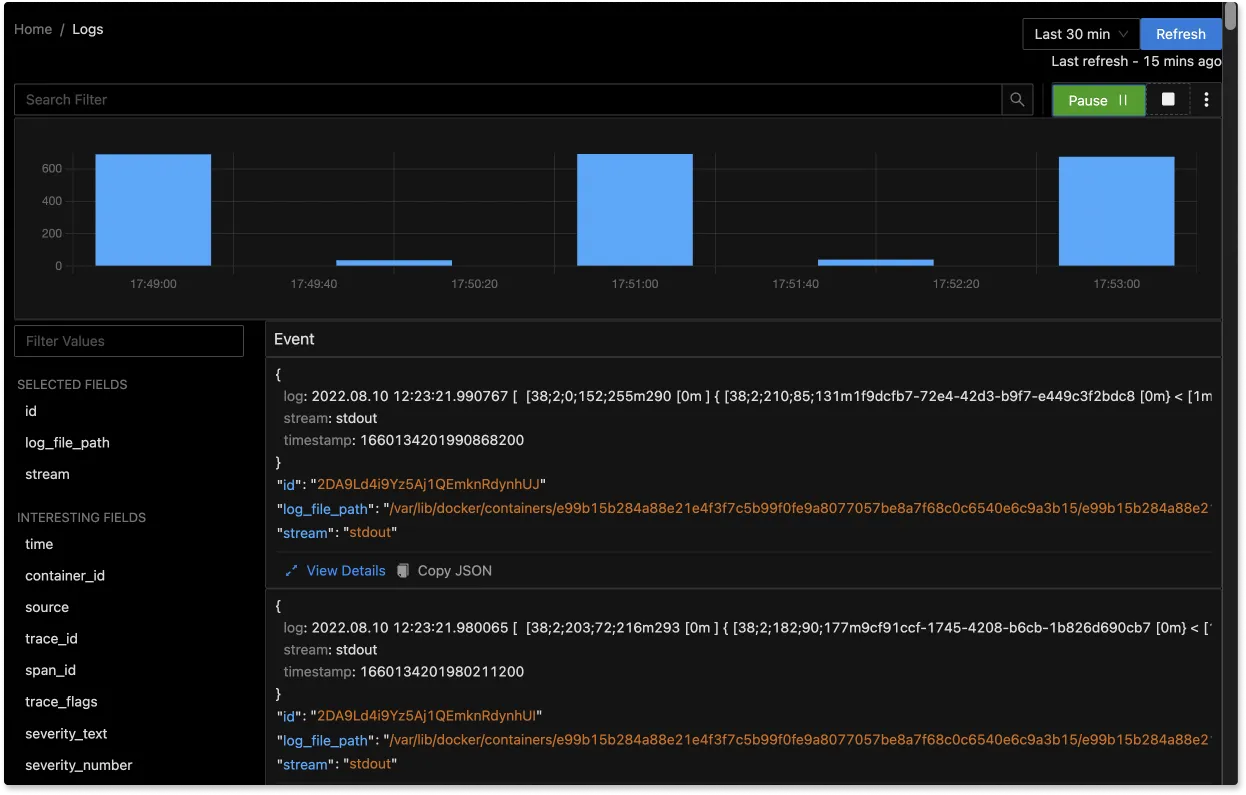
The logs tab in SigNoz has advanced features like a log query builder, search across multiple fields, structured table view, JSON view, etc.
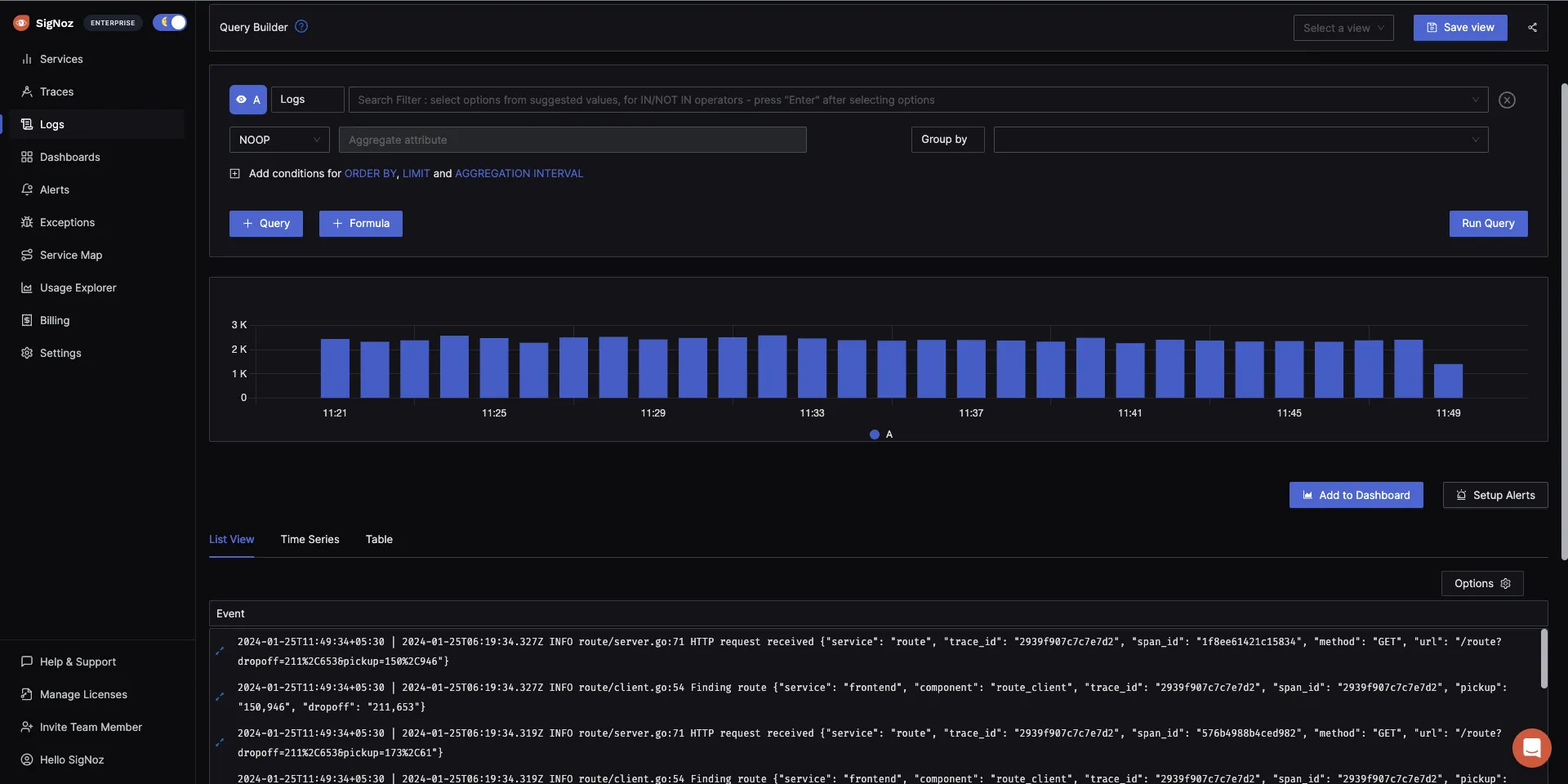
You can also view logs in real time with live tail logging.
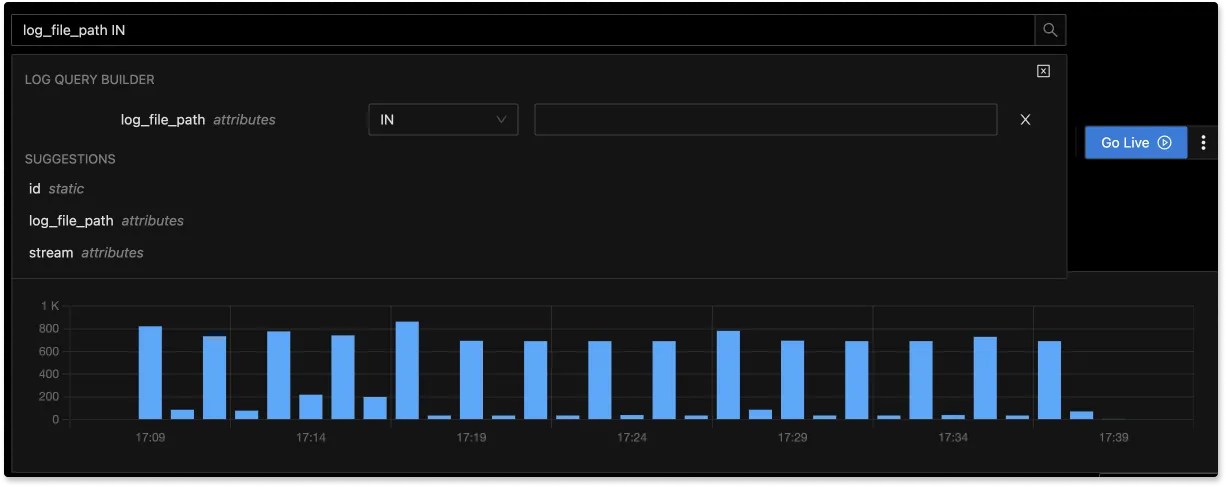
With advanced Log Query Builder, you can filter out logs quickly with a mix and match of fields.
Getting Started with SigNoz
SigNoz can be installed on macOS or Linux computers in just three steps by using a simple install script.
The install script automatically installs Docker Engine on Linux. However, on macOS, you must manually install Docker Engine before running the install script.
git clone -b main https://github.com/SigNoz/signoz.git
cd signoz/deploy/
./install.sh
You can visit our documentation for instructions on how to install SigNoz using Docker Swarm and Helm Charts.
If you liked what you read, then check out our GitHub repo 👇
Related Posts



